Jean Baptiste Huet
(1745-1811)
Jean Baptiste Huet was a French versatile artist of the second halh of the 18th century. He was a painter, an engraver and a designer. He had a close collaboration with the textile manufacturer J-C Oberkampf from 1783 to 1811. His style, influenced by Francois Boucher , was typical of the return to nature fashion of the second half of the 18th century.

Biography
Jean Baptiste Huet was born in 1745 in a family of artists. His grandfather Christophe and his own father Nicholas were both painters. He was an apprentice at the workshop of Charles Dagomer , an animal painter( see below) and later with Jean Baptiste Leprince a leading student of the great painter, (1703-1770).

Around 1764 Huet entered the studio of Jean-Baptiste Le Prince, where he further developed his skill as an engraver; most of his engravings and etchings were reproductions of his own work. In 1769 Huet was accepted at the Royal Academy as an animal painter. During the last thirty years of his life Huet focused on decorative arts, designing for Oberkampf and publishing prints after his own designs.
JB Huet connections
Christophe Huet I (born 1633): Jean Baptiste Huet grandfather . He was a painter.
Christophe Huet II (1700-1759):Jean Baptiste Huet unce.Well known for his paintings of animals ( Chateau de Chantilly, Hotel de Rohan, Paris).
Nicolas Huet: Jean Baptiste Huet father. He was a painter at the King "garde meuble".
Charles Dagomer: he was a step-uncle of J B Huet and he gave him his first painting lessons.
Gilles Demarteau: he was an engraver who worked for Boucher and J.B Huet.
Bernard de Montfaucon (1655-1741): published "L'antiquite expliquee et representee en figures" in 1719, a book that influenced Huet style.

Le couronnement de la rosière" ( the crowning of the rose maiden). The scene on the top depicts an annual country tradition in which the most virtuous young maiden was crowned with roses. ( Detroit Institute of Arts)

This Toile de Jouy fabric was printed in 1783 after a cartoon designed by Huet and named " Les travaux de la manufacture" ( Works at the factory). There are fourteen scenes describing different activities at the Oberkampf factory. The fabric printed after this cartoon was intended to promote the firm. ( Metropolotan Museum of Art)
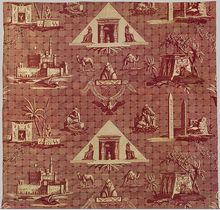
les monuments d'Egypte" 1808. Egypt became a very fashionable subject of interest in France after the Bonaparte' expedition (1798). Different scenes of Egypt are depicted: the Alexandria's harbour, Cleopatra's obelisk, Marathée's obelisk, The ruins of the famous Alexandria library and several temples. ( ( Metropolotan Museum of Art)

Jean Baptiste Huet was commissioned in 1780 from the Beauvais tapestry manufactory for the design of ten tapestries. They were a huge sucess and reproduced several times. The pastoral scene surrounded by a garland of flowers and draperies is very typical of Huet decorative style. (Le Louvre)
Further Readings: C. Gabillot, Les Huet, Jean Baptiste et ses trois fils (Paris, 1892)
|
Museums Detroit Institute of Arts
|
